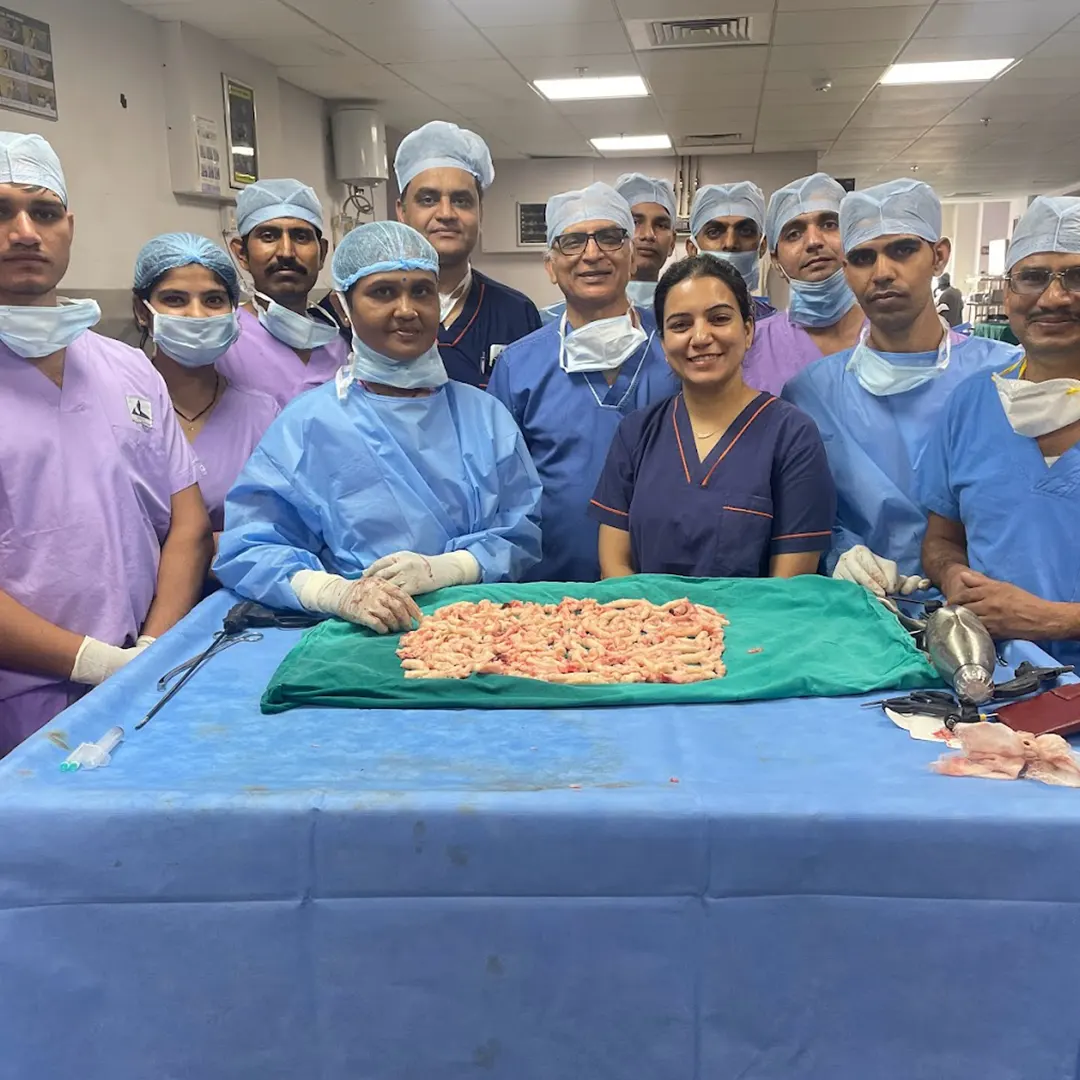
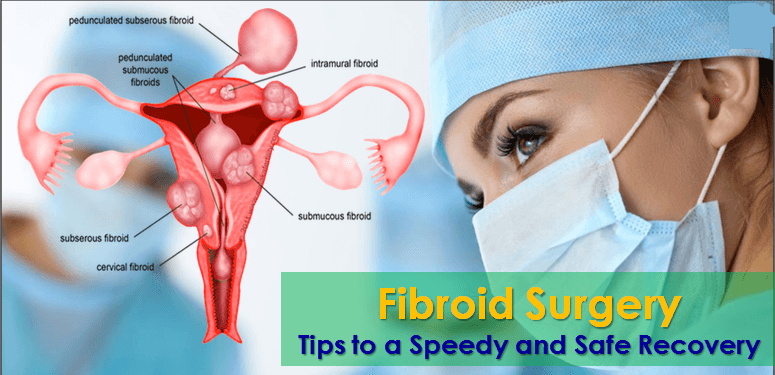
The non-cancerous growths, uterine fibroids, also called leiomyomas, are smooth benign muscular tumours that develop with the uterus’ muscular walls. The tumours can be larger and could fill the abdominal cavity or can be as small as a pea. Approximately 80% of females experience fibroids during their lifetime.
This gynecological disorder affects females during their perimenopausal and reproductive years. The types of uttering fibroids are subserosal (that grows outside the uterus), submucosal (that grows near the uttering lining), or intramural (that grows in the muscle). Although a few subserosal fibroids do not cause symptoms, submucosal and intramural fibroids may cause the most cramping and bleeding.
The symptoms of uterine fibroids vary by location, number, and size. As suggested by the leading gynecologist of Jaipur, Dr Pankhuri Gautam, learn more about fibroid removal, treatment types, and tips on post-treatment care for a healthy recovery.
Understanding Fibroid Removal
Uterine fibroids have a high likelihood of developing into cancer when women experience it after menopause when they keep growing. Careful monitoring is crucial post-menopausal and may need its removal.
Most women may not develop symptoms, while symptomatic women may experience uterine and abdominal enlargement, abdominal pain and pressure, menstrual pain, excessive menstrual bleeding, constipation, urinary issues, and pain while having sex. Fibroid removal is suggested as per the woman’s severity of symptoms and her age.
Types Of Fibroid Treatments
- Surgical Procedures
- Myomectomy
The uterus is left intact in this surgical procedure, while only the fibroids are removed. Laparotomy or a standard surgical approach (open) or laparoscopy or hysteroscopy, the less invasive procedures are used to perform myomectomy. It is performed through a “bikini cut,” a small incision through the lower abdominal skin.
Many stitch layers sew back the uterine muscle after removing fibroids. Not every woman is advised to undergo fibroids since it may cause increased blood loss and become complicated when fibroids are large and many.
- Hysterectomy
A complete hysterectomy is suggested when the fibroids become cancerous. This surgical procedure involves the removal of the uterus and is advised for women with abnormal bleeding. This process may include removing ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other surrounding tissues and organs. A menstrual period and conception are not possible after this procedure.
The types of hysterectomy are complete hysterectomy or Radical hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, supracervical hysterectomy, and complete hysterectomy.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
Small or no cuts are used during minimally invasive procedures. They have fewer complications and have a faster recovery period.
- Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE)
This procedure involves injecting tiny (sand grains-sized) particles into the blood vessels leading to the uterus. These particles shrink the fibroids by sticking to the wall of the vessel and stopping blood flow to them. A blood clot is developed that blocks the blood flow.
- Radiofrequency Ablation
This minimally invasive surgical procedure significantly reduces the size of fibroids by using heat to target them one after another. Improved life quality and fewer symptoms are experienced when fibroids are shrunk through this procedure.
- Robotic Or Laparoscopic Myomectomy
This procedure involves the removal of fibroids and visualising them using a laparoscope or lighted thin scope with a camera on its end. An incision is made to insert small instruments into the pelvis to remove fibroids. It is suggested for women having less than 15 myomas or a single one less than 15 cm in size.
- Non-Surgical treatments
– Medications
The pharmacological fibroid treatment is the non-surgical treatment option to treat uterine fibroids. A few medications prescribed to stabilise or manage uterine fibroids are as follows:
- Birth control pills
- GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) Agonists
- Antagonists
- Iron supplements
- Progestins
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including naproxen or ibuprofen.
– Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is used to reduce the symptoms and shrink the size of fibroids by blocking the effects of estrogen or reducing the production of estrogen in the body. Besides, birth control pills, Lupron, and progesterone-based pills reduce bleeding or shrink fibroids.
– Radiologic Procedures
Radiological procedures are the intervention approaches to manage uterine fibroids. The approaches are uterine fibroid embolisation (UFE) or uterine artery embolisation (UAE), where an embolisation approach with permanent embolic embolisation stops blood flow to these abnormal growths. It shrinks fibroids and reduces bleeding.
Fibroids: Post-Treatments Recovery Timeline
- Myomectomy: The recovery time for myomectomy is about four to six weeks since it may require rest for some women while others may experience little pain.
- Hysterectomy: Hysterectomy takes about a month or six weeks to recover and may vary based on the hysterectomy type.
- Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE): It takes about two to five weeks to recover completely after Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE). The blood loss is less during the procedure and does not necessitate general anaesthesia.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: It takes about two weeks to relieve pain after radiofrequency ablation, which is caused by muscle spasms or residual nerve ablation effects. However, people often recover within a day or two since pain relief is immediate and relief lasts for about six months to one year.
- Robotic Or Laparoscopic Myomectomy: This procedure requires about two or four weeks to recover. Since small incisions cause less pain, people may recover quickly.
- Radiologic Procedures: This requires one or two weeks for patients to recover and return to their daily schedule. However, about two or three months are required to shrink fibroids enough to improve pressure and pain.
Post-Treatment Care For Fibroids: Tips For A Healthy Recovery
- Food Diet Recommended Post-Fibroid Treatment
Food options advised post-fibroid treatment help improve the associated symptoms. The suggested food choices are whole-grain foods, fruits, and vegetables. Some foods that reduce the risk of abnormal growth or developing fibroids are tomatoes, apples, cabbage, broccoli, or other cruciferous vegetables.
- Dietary Precautions Post Fibroid Treatment
Dietary precautions are crucial after surgical procedures to treat uterine fibroids to maintain balanced well-being. Some of the food types that you must stay away from are red meat, dairy products, high salt, saturated fats, and caffeinated drinks. Avoiding these foods improves recovery time and helps you return to your normal schedule faster.
- Physical Activities Post Fibroid Treatment
Swimming or gentle walking is advised for post-surgical procedures for fibroids. After 6 to 8 weeks of rest post-surgical procedure, you may start the exercises or walking, or as your specialist advises. However, weightlifting or other strenuous activities should be avoided.
- Pain Management Post Fibroid Treatment
A few of the pain management techniques post-fibroid treatment include medications, such as NSAID pills, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, naproxen, or as prescribed by your specialist.
Do’s And Don’ts After Fibroid Treatment
Do’s
- Continue workouts
- Employ stress management techniques
- Monitor blood pressure levels
- Take rest during painful menstrual periods
- Eat a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits
Don’t’s
- Avoid smoking, overconsumption of sugar
- Avoid consuming high-fat dairy products, processed foods, and red meat
Conclusion
Treating and monitoring the abnormal uterine growths called uterine fibroids is crucial for symptomatic or perimenopausal women. It alleviates them and minimizes the chances of developing cancer postmenopause. These abnormal growths may vary in size, numbers, and location, greatly depending on these factors.
Some women may require surgical procedures or medications to remove fibroids, while others may get relief from symptoms or improve by maintaining stress management, exercise, and dietary changes. Post-treatment care is crucial for women undergoing surgical procedures or therapies to recover completely and faster. Dr. Pankhuri Gautam suggests some tips in this guide to help you manage or stabilize abnormal growths, ultimately get rid of them, reduce the symptoms, and feel better.