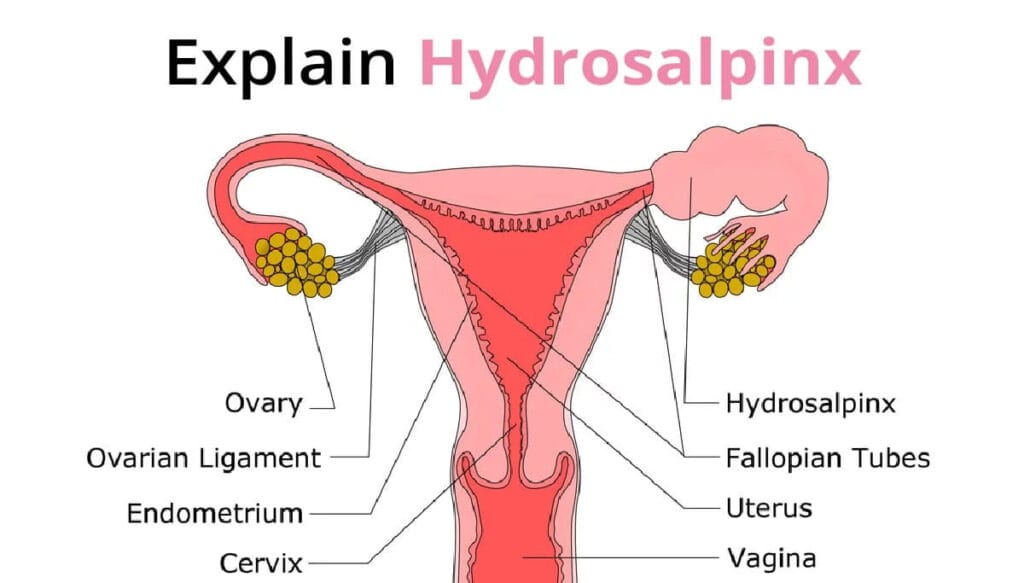
A hydrosalpinx is a condition in which the fallopian tubes are blocked, resulting in a fluid collection. The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, so any blockage in them can upset the normal functioning of the female reproductive system. If both fallopian tubes are affected, the condition is known as hydrosalpinges.
The fallopian tubes deliver the ovarian egg (ova) to the uterus during pregnancy. Therefore, blocked fallopian tubes can cause infertility. It is technically possible to get pregnant with one working fallopian tube, but pregnancy rates are lower in such cases because of the adhesions and irritations caused by hydrosalpinx.
CAUSES
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID): This infection affects the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus. It is generally caused by Chlamydia and Gonorrhea. Long-term untreated PID can cause hydrosalpinx.
ADHESIONS: Adhesions from previous surgeries involving the pelvic area can also cause hydrosalpinx.
APPENDICITIS BURST: Appendicitis burst may lead to infections in the pelvic area and can thus cause hydrosalpinx.
SYMPTOMS
In most cases, the patient may not experience any symptoms and may come to know about the condition only after diagnosis of infertility.
INFERTILITY: Infertility is a significant symptom of hydrosalpinx.
PAIN & ABNORMAL DISCHARGE :
Pelvic pain and abnormal vaginal discharge are experienced in some cases.
SYMPTOMS OF THE ROOT CAUSE: The patient may experience the root cause symptoms, such as pain in the lower abdominal area or motion tenderness in the case of PID.
DIAGNOSES
The diagnosis of hydrosalpinx may involve a hysterosalpingogram (HSG), ultrasound or laparoscopy.
TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND: Ultrasound is an imaging technique that uses ultrasound waves to create an image/video of the patient’s internal organs. In transvaginal ultrasound, the doctor will insert the transducer into the patient’s vagina to inspect the uterus with the help of the video/image on screen.
HSG: In many cases, ultrasound may not be able to show the blockage. Hence, to ascertain hydrosalpinx, the doctor may recommend sonohysterosalpingography. It is a procedure similar to ultrasound, but in this procedure, the surgeon also inserts a saline solution into the cavity of the uterus. This helps the doctor see things that would not be possible with normal ultrasound.
LAPAROSCOPY: Diagnostic laparoscopy may help determine hydrosalpinx and rule out other conditions. It is a procedure in which a small, lighted instrument known as the laparoscope is inserted through small incisions near the abdomen area. The instrument relays video to a screen, which helps the doctor inspect the uterus and fallopian tubes.
TREATMENT
The course of treatment depends on the extent of the condition and the patient’s preferences.
NEOSALPINGOSTOMY: If the blockage is minor, repairing it may be an option. In such instances, the patient can conceive naturally. The blockage is removed via a laparoscopy.
REMOVAL OF FALLOPIAN TUBES: The fallopian tubes are removed in this procedure. Hence, natural childbirth is not possible. IVF – in vitro fertilization is used to conceive.