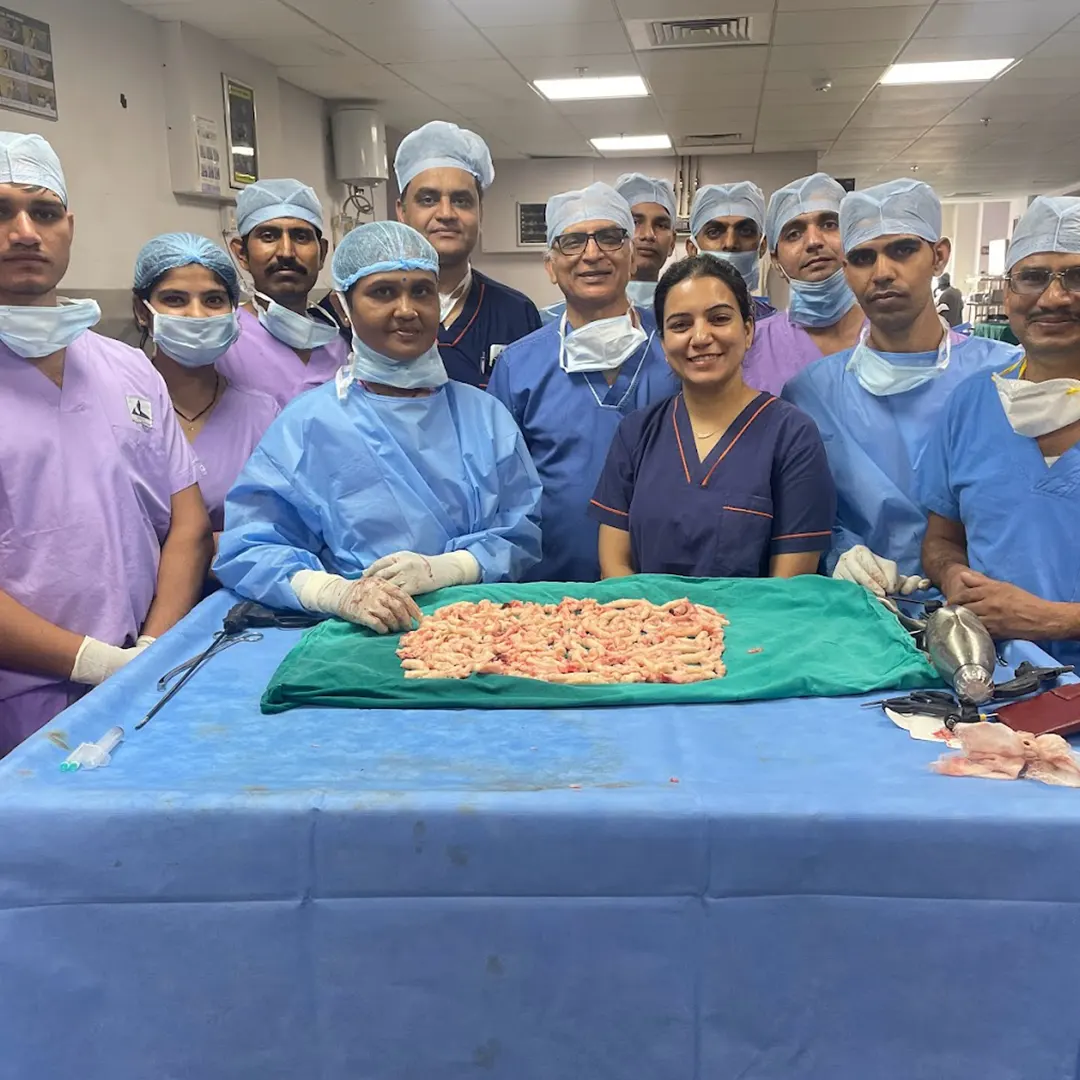
Very common growths, Fibroids, grow and develop in about 20% to 70% of females during their reproductive years. Most of the time, these growths are harmless, yet avoiding them may result in health implications, particularly infertility.
Fibrosis may cause many reproductive issues, excessive bleeding, or other complications, so managing these common growths is crucial for general well-being. Let us check this guide and understand how Dr Pankhuri Gautam, the top gynecologist in Jaipur, and specialist in treating fibroblasts, advises choosing the right fibroblast treatment and helping people handle and treat these common growths.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
The fibroids, non-cancerous growths, and Uterine Fibroids, form or grow in the uterus. Leiomyomas, often called uterine fibroids, are tissue and muscle and are among the most common non-cancerous tumors found in assigned females at birth (AFAB) and women.
They occur mostly between 40 to 80 percent of individuals having a uterus aged from 30 to 50 years. These growths are not found in those who entered menopause or did not experience the first menstruation cycle or monthly periods. Fibroids can grow in a cluster with sizes ranging from 1 mm or above 8 inches (20 cm) or as one growth (single nodule).
The main uterine fibroid types include the following:
- Submucosal fibroids: The common growths or Fibroids are named submucosal fibroids when they grow in the uterine cavity.
- Subserosal fibroids: These growths are called subserosal fibroids when they grow outside the uterus.
- Intramural fibroids: These are among the most common fibroid types, called intramural fibroids when they grow inside the uterus’ muscular wall.
- Pedunculated fibroids: It is the least common fibroid type attached with a stem or stalk to the uterus. These growths appear in a mushroom shape since they have a wider top and stalk.
Fibroid Symptoms –
Fibroid treatment is usually based on the symptoms experienced. Some women dealing with fibroids may be non-symptomatic, while others may have symptoms, including the following:
- Abdominal enlargement or increased abdominal distention
- Bleeding between the menstrual periods
- Feeling full or bloating in the abdomen or lower belly
- Frequent urination
- Irregular, painful, and excessive vaginal bleeding during menstrual periods
- Low back ache or pain during intercourse
Note: When hormonal levels decline in the body after menopause, the uterine fibroids symptoms often heal or stabilize.
Choosing The Right Treatment Based On:
1. Overall Health And Medical History
Your overall health and medical history greatly affect the fibroid treatment choice. Some medications used for health conditions may interfere with treating fibroids. Therefore, check with your specialists for the right fibroid treatment based on your health condition and medical history.
2. Fertility Desires
A few surgical procedures may interfere with your fertility desires as they may remove the uterus and ovaries. You may check with the specialist and consider the option that may help you conceive in the future.
3. Symptom Severity
When the severity of the symptoms is less or mild, you may monitor the growth and size of fibroids and consider the treatment option as advised.
4. Fibroid Size And Location
The right treatment choice often depends on the fibroid size, location, and number of fibroids. If the size and number of fibroids decrease, you may get relief from medications or therapies. However, when the fibroid size is large and deeper, a surgical procedure is suggested.
Recovery And Aftercare
1. Follow-Up Appointments And Monitoring
Follow-up and monitoring are crucial after fibroid treatment to avoid post-treatment symptoms and further complications. Since fibroids may return or grow with multiple fibroids, monitoring, and follow-up will help you manage them.
2. Lifestyle Modifications For A Healthy Recovery
Lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, stress management, maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough sleep, and limiting caffeine and alcohol, and dietary modifications like focusing on whole foods, increased fibre intake, staying hydrated, limiting processed foods, red meat, and refined carbs may help in healthy recovery and make you feel better. Natural approaches are safer and faster recovery options after fibroid treatment.
3. Post-Treatment Recovery Expectations
It takes about four to six weeks to recover after fibroid treatment completely.
Fibroids Medical Evaluation
Consultation With A Healthcare Provider
Consultation with a healthcare provider will help you determine the severity of uterine fibroids and symptoms that may need to be addressed immediately. It will help you get medications to relieve specific symptoms and a few examinations to determine the fibroid numbers and size.
Diagnostic Tests For Fibroids
- Ultrasound- The pictures of the uterus are created through this test using sound waves. This test measures and maps the fibroids after confirming their growth. A transducer is an ultrasound device a technician or specialist uses for transabdominal ultrasound over the stomach area. A transvaginal ultrasound is performed when the images of the uterus are obtained by placing the device inside the uterus.
- MRI- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) exhibits additional details of fibroids, including their location and size. This imaging is performed for people nearing menopause (perimenopause) or having a large uterus. It also determines fibroid treatment choices and identifies different tumor types.
- Hysteroscopy- A hysteroscope or a lighted small telescope is used to examine the uterus through the cervix. Saline injected during this test expands the uterine cavity space to examine the openings and uterine walls of the fallopian tubes.
- Biopsy (if needed) – The tissue sample is collected by performing a biopsy under local anesthesia. The sample is collected from the uterus by inserting an instrument passing through the cervix. The tissue sample is examined in a laboratory under a microscope.
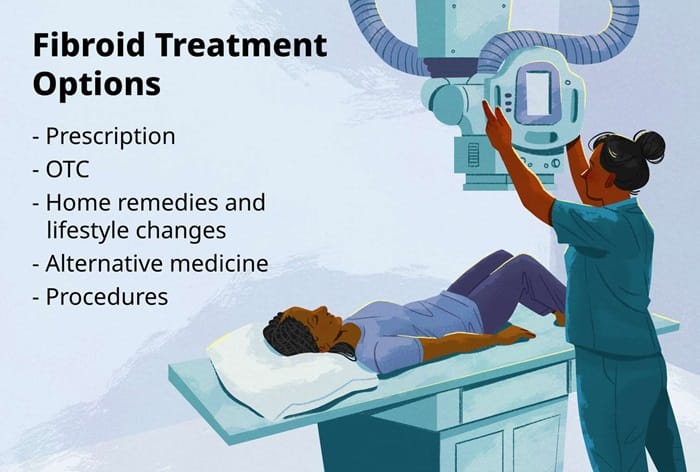
Fibroid Treatment Options
- Watchful Waiting
1. When Is Watchful Waiting Appropriate?
Watchful waiting is appropriate when you don’t experience or have any mildly disturbing symptoms associated with fibroids. Since fibroids are non-cancerous, they do not interfere with conceiving and often go away after menopause.
2. Monitoring Symptoms And Growth
Monitoring symptoms and growth of uterine fibroids is crucial when you experience frequent urination, excessive bleeding, and low back ache. MRI screening or ultrasound can help you identify its growth and the treatment needed for managing fibroids.
- Medications For Fibroid Treatment
1. Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal therapy shrinks the fibroids before undergoing surgical procedures or temporarily relieves menstrual pain and excessive menstrual bleeding. Some of the hormonal therapies are the following:
- Estrogen and progestin combination (birth control medications)
- Progestin (progestin medications and hormonal intrauterine device)
- Ulipristal acetate
- GnRH (nasal sprays and injections)
2. Non-Hormonal Medications
Non-hormonal medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are given to get relief from fibroids-related pain, yet do not reduce bleeding due to these growths. Some of the commonly prescribed non-hormonal medications for fibroids are the following:
- Naproxen sodium (Aleve)
- Ibrufen (Motrin IB, Advil, etc)
- Iron and vitamin pills for anaemia and excessive menstrual bleeding
- Non-Surgical Procedures
1. Uterine Artery Embolisation (Uae)
Embolic agents are small particles injected during this process in those arteries that supply blood to the uterus. These particles destroy fibroids or shrink them by cutting off the blood flow. However, when the blood supply to the organs or ovaries is reduced, it may cause some complications.
2. Radiofrequency Ablation
The heat generated in this procedure through the radiofrequency energy shrinks the feeder blood vessels and destroys uterine fibroids. Laparoscopy, a surgical procedure, is done by cutting a small area of the stomach.
It is performed as a transcervical procedure through the cervix or as a transvaginal procedure performed through the rough vagina. The needle of the tool inserted into the fibroids destroys fibroid tissue immediately.
3. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (Hifu)
This procedure is performed through an MRI machine that generates sound waves. The specialist focuses on fibroid’s one small section and heats the target areas above 100֯F, safely destroying uterine fibroids.
- Surgical Procedures
- Myomectomy
This surgical procedure removes fibroids by a large cut in the abdomen or stomach area. It is suggested when very deep, larger, and multiple fibroids are present. However, the scarring during the surgical procedure may interfere with or reduce the future chances of conceiving a child.
- Hysterectomy
The permanent solution for uterine fibroids is removing the uterus through Hysterectomy. This procedure eliminates the chances of conceiving. This process may bring menopause when ovaries are also removed during the procedure.
Choosing The Right Treatment Based On:
- Overall Health And Medical History
Your overall health and medical history greatly affect the fibroid treatment choice. Some medications used for health conditions may interfere with treating fibroids. Therefore, check with your specialists for the right fibroid treatment based on your health condition and medical history.
- Fertility Desires
A few surgical procedures may interfere with your fertility desires as they may remove the uterus and ovaries. You may check with the specialist and consider the option that may help you conceive in the future.
- Symptom Severity
When the severity of the symptoms is less or mild, you may monitor the growth and size of fibroids and consider the treatment option as advised.
- Fibroid Size And Location
The right treatment choice often depends on the fibroid size, location, and number of fibroids. If the size and number of fibroids decrease, you may get relief from medications or therapies. However, when the fibroid size is large and deeper, a surgical procedure is suggested.
Recovery And Aftercare
- Follow-Up Appointments And Monitoring
Follow-up and monitoring are crucial after fibroid treatment to avoid post-treatment symptoms and further complications. Since fibroids may return or grow with multiple fibroids, monitoring and follow-up will help you manage them.
- Lifestyle Modifications For A Healthy Recovery
Lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, stress management, maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough sleep, and limiting caffeine and alcohol, and dietary modifications like focusing on whole foods, increased fibre intake, staying hydrated, limiting processed foods, red meat and refined carbs may help in healthy recovery and make you feel better. Natural approaches are safer and faster recovery options after fibroid treatment.
- Post-Treatment Recovery Expectations
It takes about four to six weeks to recover after fibroid treatment completely.
Conclusion
The abnormal yet common growths inside or outside the uterus are fibroids, commonly referred to as myomas or uterine fibroids. These growths are not a threat to life or cancerous, yet may lead to specific health complications and issues. The right fibroid treatment choice is crucial to manage these abnormal growths based on their location, size, and numbers. Dr. Pankhuri Gautam can suggest the right treatment choice based on your health condition, fertility desires, fibroid type, severity of symptoms, number, location, and size.